8. Videos zu ausgewählten Experimenten
Nr. | Titel / Beschreibung - zu Video | aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaScreenshotsaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa |
8.1 | HalbmikrotitrationUrinsteinentferner (HCl) wird mit Natronlauge titriert | |
8.2 | SauerstoffnachweisKleinste Sauerstoffmengen werden mit Eierfarbe nachgewiesen | |
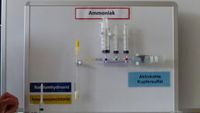
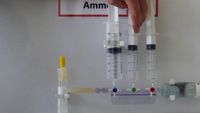
8.3 | Synthese von AmmoniakHerstellen von Ammoniak aus Ammoniumchlorid und Natriumhydroxid | |
8.4 | Ammoniak-SpringbrunnenAmmoniak reagiert heftig mit Wasser | |
8.5 | Reduktion von Kupfer(II)-oxid 1Kupferoxid wird mit Wasserstoff reduziert | |
8.6 | Reduktion von Kupfer(II)-oxid 2Kupferoxid wird mit Flüssiggas reduziert GefBU Reduktion von CuO mit FZ-Gas | |
8.7 | Reduktion von Kupfer(II)-oxid 3 Kupferoxid wird mit Flüssiggas reduziert (Variante nach Grofe) | |
8.8 | Druckabhängigkeit der Siedetemperatur 1 (Flüssiggas) Die Siedetemperatur von Flüssiggas wird mit Hilfe einer Einhandzwinge erniedrigt | |
8.9 | Druckabhängigkeit der Siedetemperatur 2 (Flüssiggas)Die Siedetemperatur von Flüssiggas (Komet) wird mit Hilfe einer Vakuumspritze an Haltestange erniedrigt | |
8.10 | Druckabhängigkeit der Siedetemperatur 1 (Wasser)Wasser siedet bei Unterdruck in einer Vakuumspritze im Wasserbad | |
8.11 | Druckabhängigkeit der Siedetemperatur 2 (Wasser) Wasser siedet bei Unterdruck in einer Vakuumspritze im Wasserbad (2 Thermometer) | |
8.12 | Mg und HCl quantitativ (Variante 1) Bestimmung des Wasserstoffvolumens bei der Reaktion von HCl mit Mg (z.B. zur Bestimmung der Molaren Masse von Mg) | |
8.13 | Mg und HCl quantitativ (Variante 2) Bestimmung des Wasserstoffvolumens bei der Reaktion von HCl mit Mg (z.B. zur Bestimmung der Molaren Masse von Mg) | |
8.14 | Reaktion von SO2 und O2 zu SO3 | |
8.15 | Cl2 aus HCl(aq) und KMnO4 | |
8.16 | Reaktion von Natrium mit Chlor | |
8.17 | KalkwasserherstellungPreisgünstige Methode zur Herstellung von Kalkwasser | |
8.18 | DiamantverbrennungEcht oder Fälschung? Ein Diamant verbrennt im Sauerstoffstrom | |
8.19 | ||
8.20 | Aufbau und Startphase | |
8.21 | nach 30 Minuten | |
8.22 | Katalytische Zersetzung von H2O2(aq) (1) Das (nicht-glühende) Platin-Herz als Katalysator | |
8.23 | Katalytische Zersetzung von H2O2(aq) (2) Platin-Drähte und Braunstein Körner/Pulver als Katalysatoren | |
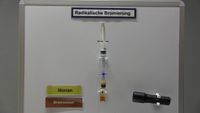
8.24 | Bromierung von Nonan: Brom-Wasser + Nonan | |
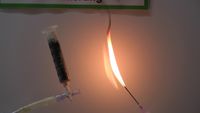
8.25 | Eliminierung von tert. Butylalkohol: Reaktion mit Schwefelsäure |